The new measure, adopted on January 20th by Parliament, was signed into law by President Alexander Van der Bellen on Friday, the culmination of a process that began in November in the face of the rapid spread of the Omicron variant.
The government decided to pursue its new tougher approach despite criticism within the country.
“No other country in Europe is following us on compulsory vaccines,” said Manuel Krautgartner, who has campaigned against the new approach.
In neighbouring Germany, a similar law championed by the new Social Democrat Chancellor Olaf Scholz was debated last month in the Bundestag, or lower house of parliament, but has not made progress yet due to divisions within the political class.
Checks from mid-March
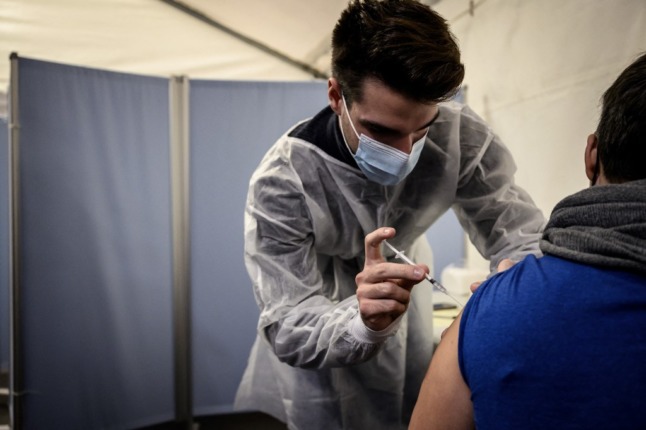
Despite the threat of such a drastic measure, the vaccination rate in Austria has still failed to take off, languishing below the levels seen in France or Spain.
The humanitarian association Arbeiter Samariter Bund, which oversees some vaccination sites in the capital Vienna, said there had an uptick in turnout this week.
“We recorded a small increase of around nine percent compared to last week,” the organisation’s manager, Michael Hausmann, told AFP.
From the average of around 7,000 injections administered every day in the capital, only 10 percent are a first dose, he said.
Erika Viskancove, a 33-year-old accountant, said she came to a vaccination centre situated next to an Art Deco swimming pool to receive her third booster dose.
“I sincerely believe that the law is the best way” to defeat the pandemic, she said, calling on other countries to follow Austria’s lead.
Melanie, a 23-year-old waitress who preferred not to give her second name, said she was mainly there to avoid ending up “locked up at home”.
Non-vaccinated people are currently excluded from restaurants, sports and cultural venues.
But from now on they will also be subject to fines, which Melanie said was “unhealthy”.
The law applies to all adult residents with the exception of pregnant women, those who have contracted the virus within the past 180 days and those with medical exemptions.
Checks will begin from mid-March, with sanctions ranging from 600 to 3,600 euros ($690-$4,100).
They will, however, be lifted if the person fined gets vaccinated within two weeks.
Protect against new variants
Waiting in the queue, others say they are in favour of vaccination for all.
“We would have finished a long time ago (with the pandemic) if everyone had been vaccinated”, said legal worker, Angelika Altmann.
More than 60 percent of Austrians support the measure, according to a recent survey, but large swathes of the population remain strongly opposed.
For several weeks after the announcement of the new law, tens of thousands of people took to the streets to protest against what they regard as a radical and draconian policy.
Critics have also questioned the need for compulsion given the far milder nature of the Omicron variant.
Conservative Chancellor Karl Nehammer, who leads the Alpine country with the environmentalist Greens, also announced at the same time a relaxation of earlier Covid-19 restrictions.
But for Health Minister Wolfgang Mueckstein, compulsory vaccination is aimed at both protecting the country against new waves and fighting new variants.
Vaccination passes are now a reality in an increasing number of countries for certain professions or activities.
In Ecuador, it is compulsory, including for children over the age of five, a world first.
Before that, two authoritarian states in Central Asia — Tajikistan and Turkmenistan — mandated vaccination, as did Indonesia, even if less than half the population is actually vaccinated.
READ MORE:


 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
It is sad that Austria goes the exact opposite way to many other countries by fining perfectly healthy human beings who do not want to take a vaccine that has been on the market just under 2 years. Hopefully their people wake up and realize that this is not necessary and even at the very least psychologically harmful.
Totally agree. It’s a slippery slope for those who don’t learn from history gladly embrace. I guess 80 years after the fascism of NAZI Germany is long enough to repeat without much opposition.