Italy’s motorways (or autostrade) rarely see much in the way of heavy traffic on regular weekdays or weekends. But that all changes around national public holidays as hundreds of thousands of people take to the road to reach their chosen holiday destinations.
That’s why Italy’s State Police (Polizia di Stato) issues traffic warnings ahead of all of Italy’s major holidays, including Easter weekend, and even publishes its own calendar showing when traffic is predicted to be at its worst.
The calendar is colour-coded, with a yellow marker indicating heavy traffic, red indicating heavy traffic with ‘possible critical conditions’, and black indicating ‘critical’ traffic.
As some 10.5 million people in Italy are currently expected to travel for the upcoming vacanze di pasqua, Italian roads are expected to see heavy traffic over the long weekend, though some days (and times) will be worse than others for motorists.
When is traffic most likely?
Good Friday, which is generally when most people in Italy leave for their Easter getaways, is expected to be marked by heavy traffic in the morning, with possible critical conditions in the second half of the day.
Potentially critical congestion is expected to continue into the morning of Saturday, March 30th, though overall traffic should slightly improve in the afternoon.
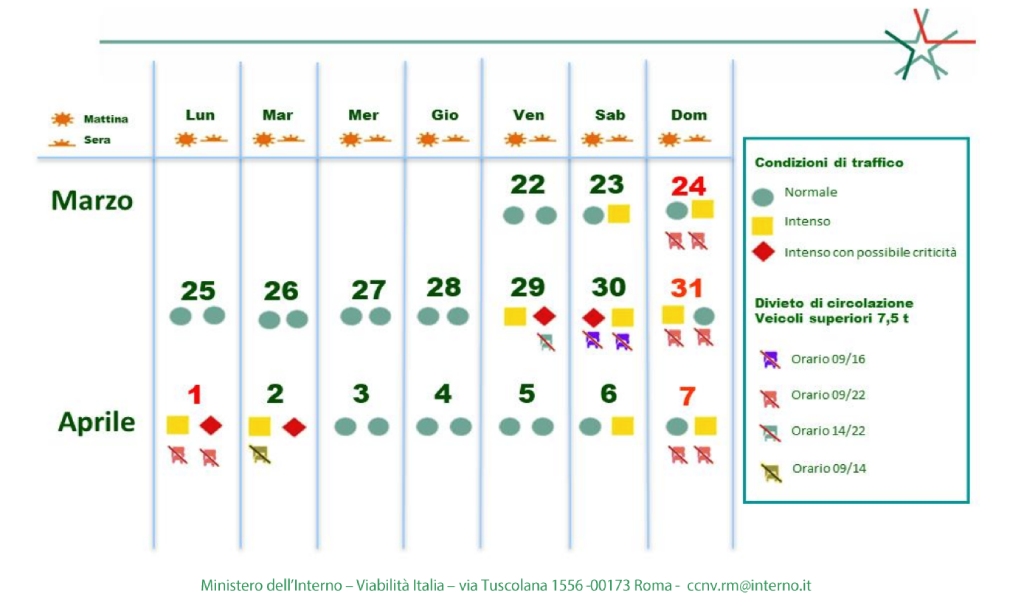
As in previous years, Easter Sunday should be a better day for drivers as most Italians tend to focus on their family lunches rather than travelling on the day. Some roads, however, may still see intense traffic in the morning.
Unsurprisingly, the whole of Easter Monday (or pasquetta in Italian) is expected to be marked by heavy traffic, with possibly critical conditions in the afternoon and evening.
Many Italians will take a trip out of town (the so-called gita fuori porta) on the day, which is likely to result in intense traffic on many routes, especially roads connecting big cities to popular seaside or countryside locations.
On top of that, pasquetta officially closes the Easter holidays, which means that many of those who spent the long weekend away from home will likely be making the journey back on Monday afternoon or evening.
READ ALSO: How to pay Italian traffic fines from abroad
Heavy traffic is expected to persist in the morning of Tuesday, April 2nd, with the situation forecast to worsen in the afternoon.
Travel on Italian roads should only return to normal conditions on Wednesday.
Which roads are most likely to see heavy traffic?
Motorways connecting the north of the country to the south are the most likely to experience heavy traffic over the Easter holidays as many Italians will return to their hometowns to spend time with family and friends.
Motorway A1, which connects Milan to Naples, and Motorway A14, connecting Bologna to Taranto, are both likely to see traffic jams over the long weekend, especially on Good Friday and Easter Monday.
But drivers may also come across heavy traffic on the following routes:
- A4 Turin – Trieste
- A6 Turin – Savona
- A7 Milan – Genoa
- A10 Genoa – Ventimiglia
- A12 Genoa – Rosignano
- A22 Brenner Pass – Modena
- A24 Rome – Teramo
Major state roads (or strade statali in Italian) connecting big cities to popular coastal or countryside locations may also be affected by heavy traffic, especially on Easter Monday.
Useful information for travellers
If you’re planning on travelling this weekend, there are a number of resources that you can use to keep up to date with the latest developments on the road.
This online map from Italy’s motorway construction and maintenance company ANAS features live updates on road closures, maintenance work, traffic levels and even weather conditions. The service is also available through their mobile app, ‘VAI’.
READ ALSO: What is Italy’s Telepass and how do you use it?
Motorway company Autostrade per l’Italia offers a similar live map (also available in English), showing road closures and traffic jams as well as the locations of the nearest petrol stations and service areas.
Finally, if you’d like to speak directly with an operator while you’re on the road, you can do so by either contacting ANAS’s customer service at 800 841 148 or calling the Transport Ministry’s info centre (CCISS) at 1518.



 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments