In a car-loving country like Germany, it seemed like an impossible scenario: motorists being forced to leave their cars at home on the weekend and rely on bikes or public transport instead.
This, however, was exactly the prospect raised by Transport Minister Volker Wissing recently. In a letter to leaders of the governing Social Democrats (SDP), the Greens and Free Democrats (FDP), the FDP politician piled more pressure on the government to ease the climate protection rules.
READ ALSO: German minister threatens to introduce weekend ‘driving ban’
If they didn’t do it soon, he said, drastic measures like a driving ban on Saturdays and Sundays would be needed.
In just a matter of days – and after sending the media into a frenzy – Wissing got what he wanted. On April 15th, the coalition government announced that they had reached an agreement on their climate protection reforms. The Bundestag approved the reforms on Friday April 26th.
Once the new rules come in, government ministers like Wissing will be under far less pressure to hit annual climate targets and can instead rely on other sectors to reduce their emissions instead.
How are the rules being relaxed?
Under the current Climate Protection Act, damaging emissions like CO2 and methane gas in energy-intensive sectors are measured on an annual basis. The sectors that are monitored include energy, housing, transport, industry, waste-disposal and agriculture.
These sectors are all given an annual emissions ‘budget’ with the ultimate aim of cutting Germany’s emissions 65 percent by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
If a particular sector, like transport, fails to reduce its emissions in any given year, ministers are legally obliged to introduce what’s known in German as a Sofortprogramm – a package of emergency measures designed to rapidly cut emissions – the following year. They are given three months from the release of the emissions data to do so.
Under the new law, the government will stick track emissions across different sectors, but the bar for introducing emergency measures will be much higher. That’s because the government will look at the full picture and allow different sectors to ‘pool’ their emissions savings, for example by relying on lower emissions in the housing sector to offset increases in agriculture.
READ ALSO: Where (and when) is traffic the heaviest in Germany?
At the same time, sectors like transport will only face consequences after failing to hit climate targets for two years in a row, and this package of measures will be decided by the government as a whole rather than by individual ministries.
Why is this happening now?
Just a few hours before the traffic-light coalition announced that they had signed off on the climate reforms, the Expert Council for Climate Protection Issues (ERK) released official data on the emissions produced by various sectors in Germany in 2023.
As expected, the transport sector drastically overshot the amount of emissions in its budget, pumping out 146 million tonnes of CO2 and other harmful emissions rather than the permitted 133 million tonnes.
Aside from housing, which produced one million tonnes more than the allowed 101 million tonnes of emissions, transport was the only sector that missed its climate targets in 2023, and it did so for the third year running.

In total, Germany slashed its emissions by 10 percent last year, with most sectors comfortably within their respective budgets. According to the ERK, 674 million tonnes of climate-damaging emissions were produced in 2023, compared to 750 million tonnes back in 2022.
However, Wissing’s failure to reduce CO2 emissions in the transport sector for yet another year means he is legally obliged to set out his Sofortprogramm within three months.
This has made the situation much more urgent for the FDP politician.
But if the climate protection reforms come into force before July, the minister will be spared from having to take drastic action to cut emissions within his sector.
Wissing has repeatedly blocked climate protection measures such as the implementation of a speed limit on the Autobahn and is known, along with much of his party, for being a champion of car owners and a supporter of motorway expansion.
How will Germany’s climate protection reforms affect me?
While German tabloids such as Bild have responded with relief that the government has averted a driving ban, most serious commentators agree that tough restrictions on motorists were never on the table.
During the oil crisis in the 1970s, Germany briefly introduced a driving ban on Sundays, but it’s highly unlikely that this would ever be repeated in modern times.
A much more likely explanation is that Wissing wanted to use the threat as leverage to avoid emergency climate measures, while also painting the current climate protection laws as draconian and authoritarian.
A few days later, the best-selling German newspaper is still pretending that someone had seriously proposed driving bans on weekends, and that these have now been ruled out by the government coalition.
Fake news upon fake news. An entire fantasy world, almost. https://t.co/PlR3wuf2AW
— Giulio Mattioli (@giulio_mattioli) April 15, 2024
That said, it’s true that the Transport Minister seems to have steered clear of having to impose mandatory climate measures, which could have included a short or long-term ‘Tempolimit’ on the Autobahn, or other rules affecting drivers.
Instead, it seems it’ll be business as usual in the nation of car-lovers, with no clear path for cutting emissions in the transport sector.
However, there is some good news for eco-friendly homeowners, as the government has coupled its reform of the climate protection law with a new law designed to promote solar energy.
READ ALSO: How to install a solar panel on your balcony in Germany (even if you rent)
That means it should soon become easier and more affordable to erect solar panels on balconies and roofs, as well as in fields and on farmland.
For flat owners that are part of a homeowners’ association, it should also become easier to use the energy produced from solar panel installations in buildings with multiple apartments.
What are people saying?
The response to the latest climate reforms has been mixed so far, with members of the government hailing it as a necessary modernisation of the law.
Greens politician Robert Habeck, who as Economics Minister is responsible for energy and climate policy, said the new rules made the Climate Protection Act “more forward-looking, more flexible and therefore more efficient”.
At the same time, climate protection groups responded with dismay at the watering down of emissions targets, with the Environmental Association (BUND) describing the law as a “blow to the climate protection architecture in Germany”.
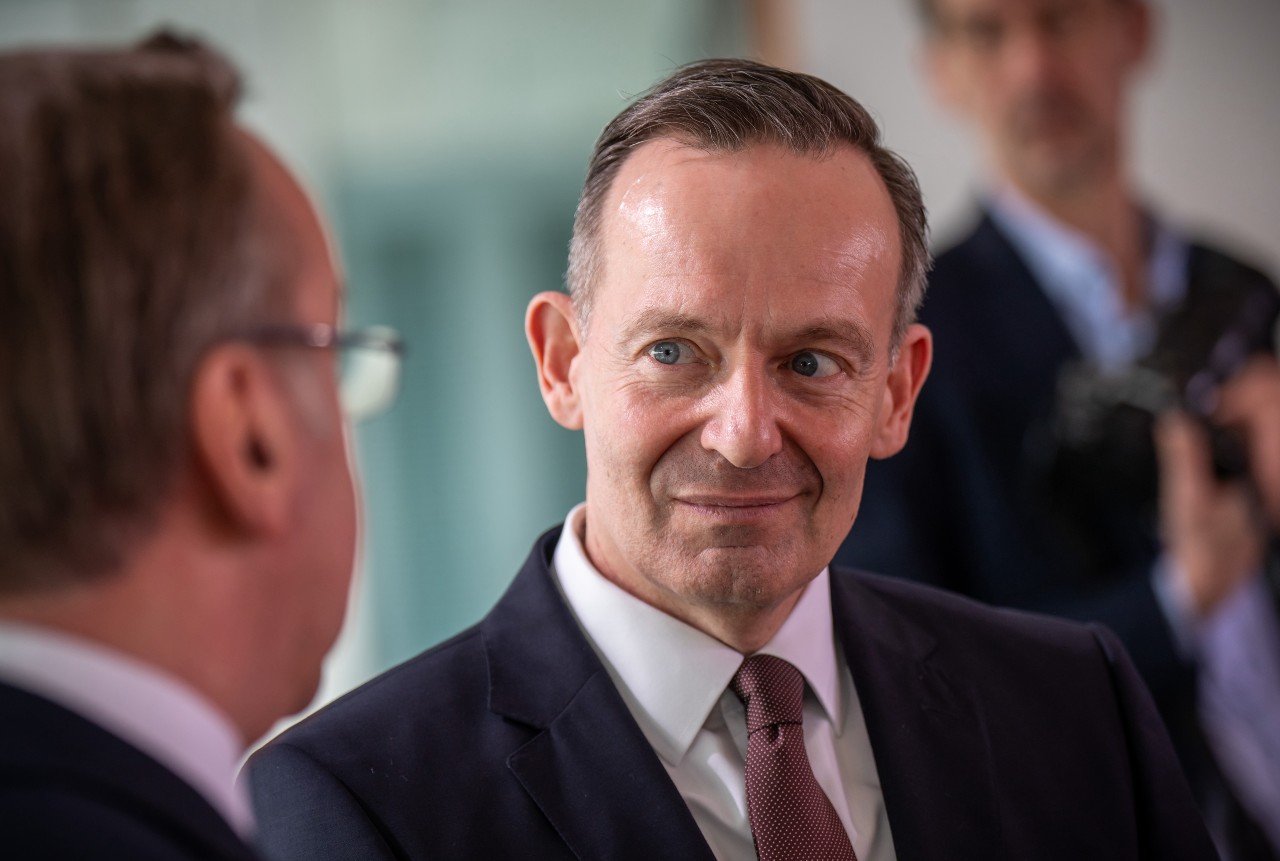

“Instead of commitment and responsibility, there is now shared irresponsibility,” BUND CEO Olaf Bandt said in a statement. “Crucial teeth have been pulled out of the law. Climate protection is to be put on the back burner with impunity.
“The traffic light government is thus underpinning its unambitious climate policy and postponing necessary climate protection until the next legislative period.”
Last year, BUND and Deutsche Umwelthilfe won a court case at the highest administrative court in Berlin-Brandenberg, with the court ordering the government to take immediate action to reduce climate emissions in the transport and housing sectors.
READ ALSO: German government loses key climate court case
The environmental protection groups recommended a series of measures, such as the scrapping of climate-damaging subsidies, the end of motorway expansion and the rapid introduction of a speed limit on parts of the Autobahn.
Their views were echoed by services union Verdi, which represents many transport-sector workers in Germany.
In a statement published ahead of the transport ministers’ conference on Wednesday, the union called for an end to subsidies for wealthy car owners, more investment in the public transport network and a guarantee for the future of the €49 Deutschlandticket.



 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments