A traditional Swedish Easter menu is very similar to a Christmas julbord, although slightly lighter, with a focus on eggs and fish rather than the winter season’s cabbage and kale dishes. Here’s our rundown of what you should expect, as well as how you can make it yourself.
Herring
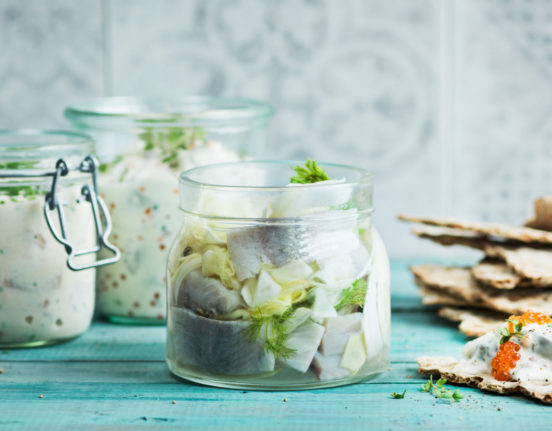
The most important part of the Easter table for many Swedes is the pickled herring (sill). In many families, one particular member of the family will be tasked with preparing the herring for the Easter meal weeks in advance.
If you’re based in Sweden, you can buy herring in the supermarket, although most will say that homemade pickled herring is superior. Vegetarian or vegan pickled herring substitutes such as svill (made from mushrooms) and tofusill (made from tofu) are also commercially available.
If you are planning on making your own pickled herring for Easter, you have a few options. Either you can buy ready-salted herring fillets in the supermarket which can be pickled straight away, or you will have to buy fresh herring fillets which you salt yourself – the latter option can take up to two weeks so requires a bit of advance planning.
You can also make your own vegetarian options: try pickling aubergine, courgette or tofu. Most recipes will take at least two days, with the herring or alternative of choice needing to marinate overnight before serving, so get planning now if you want to have it on the table for Saturday.
Here are a selection of pickled herring recipes from John Duxbury’s Swedish Food website.
Salmon
Most Easter tables will feature at least two sorts of salmon, one is often a baked side of salmon. You’ll often see smoked salmon and gravad lax (literally “buried”, preserved in salt, sugar and often dill) alongside hovmästarsås, a mustard and dill sauce which is also served at Christmas.
If you don’t eat fish, you can make a vegetarian or vegan version of gravad lax from carrots. This is usually referred to as gravad morot. Here’s a recipe (in Swedish) from the book Vegansk husmanskost by Gustav Johansson. Again, it needs to be marinated overnight, so make sure to plan this in advance.
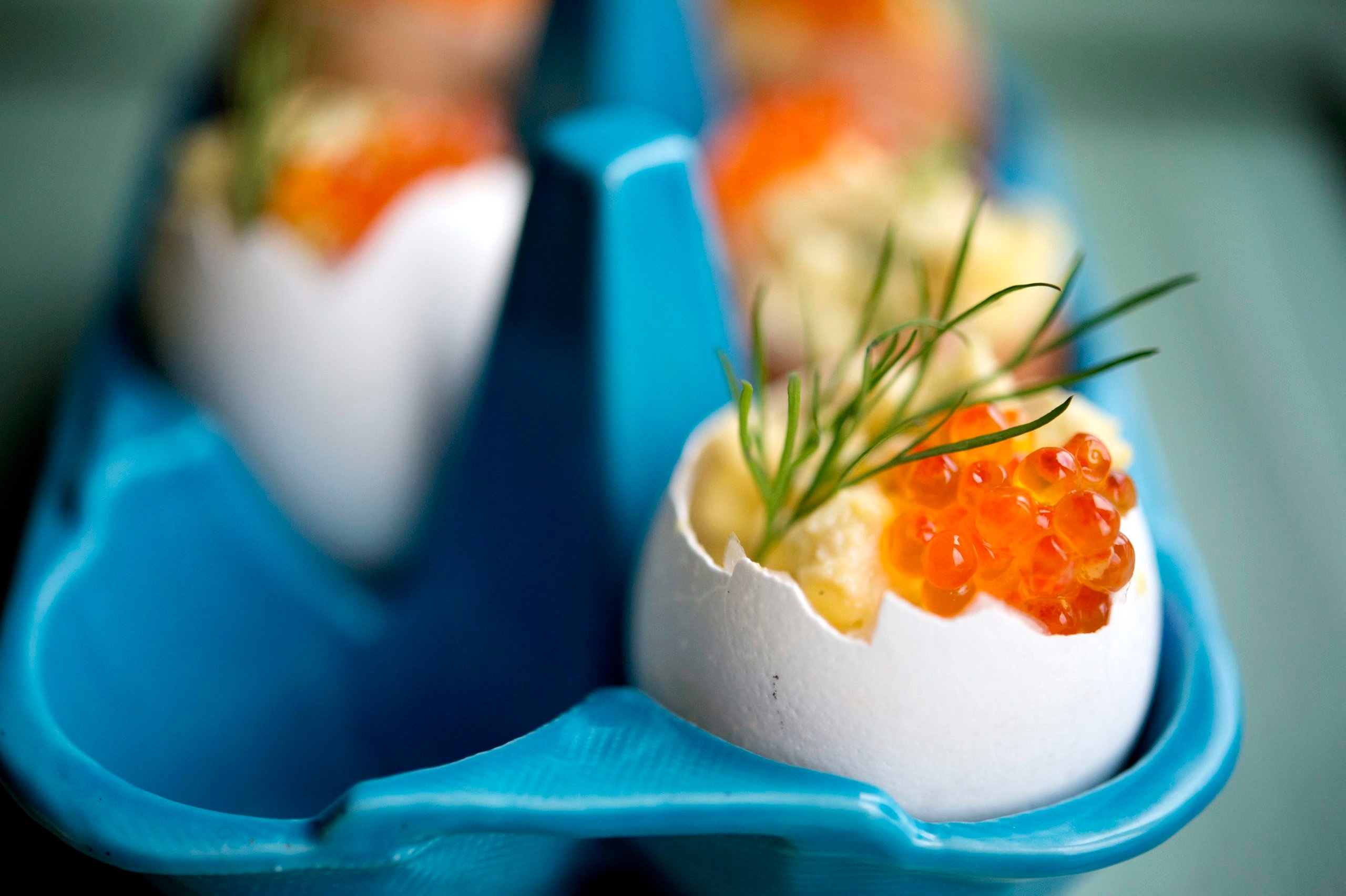
Eggs
No Easter meal would be complete without eggs. The most usual form of eggs you’ll see is cold, hardboiled eggs sliced in half. Some people will also top these half-eggs with mayonnaise, prawns and cod roe, known as kaviar in Swedish. This is sold in small glass jars in the fridge section of the supermarket, and can be orange or black – not the same as Kalles kaviar!
To make these vegetarian, you can leave out the prawns and use a vegetarian version of kaviar made from seaweed. Look for tångkaviar, which may be in the fish section of the supermarket, or the vegetarian section, if your supermarket has one of these.
If you live outside Sweden, you may be able to source tångkaviar in the food market at your local Ikea.
For a vegan option, try sliced tofu topped with vegan mayonnaise (spiked with black salt, if you can get hold of it, which will give it an eggy flavour). Top with tångkaviar and a sprig of dill and you’re good to go.
Boiled potatoes with dill
This is pretty self-explanatory. Boiled new potatoes with their skins on, served cold with dill.
Jansson’s temptation
Although more of a Christmas dish, some families also serve Jansson’s temptation, a creamy potato casserole baked in the oven, at Easter.
Jansson’s is made using Swedish ansjovis, known as sprats in English. Although it may be tempting, you should avoid substituting ansjovis with anchovies – the former are much milder and spiced, whereas the latter will be far too salty.
One option, which also has the benefit of being vegetarian, could be to use similar spices to create the same flavour you would gain from the ansjovis. Try simmering the cream used in your Jansson’s for a couple of minutes with a pinch of ground allspice, a pinch of ground cloves, a pinch of ground ginger, a pinch of white pepper and a few bay leaves instead.
Check out this Jansson’s temptation recipe from our archives.
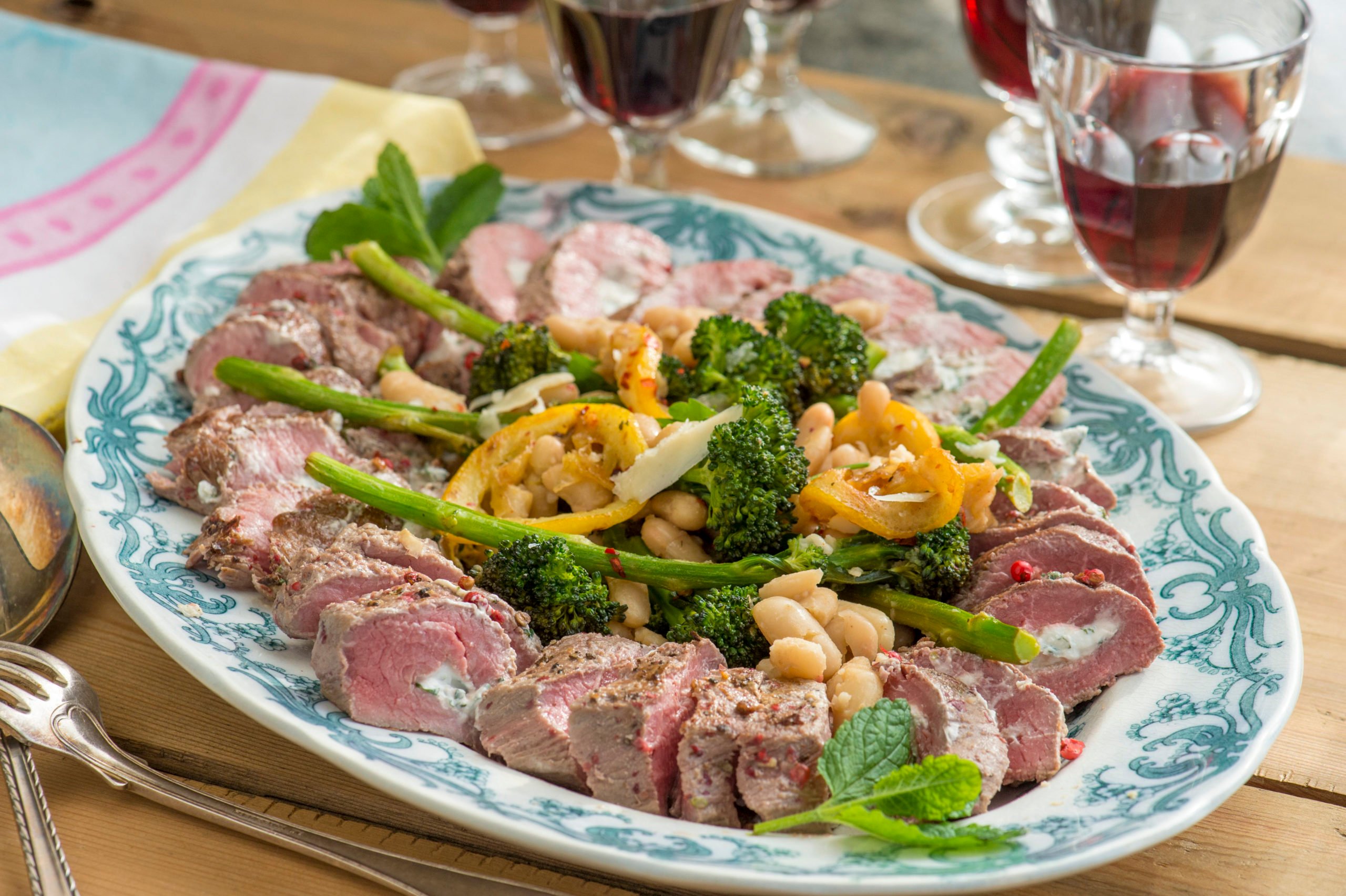
Lamb
Roast lamb is also becoming more and more popular at Easter, usually as a roast joint of lamb or a rack of lamb.
This can be difficult to make a convincing vegetarian version of, but vegetarian meatballs or sausages could be a good substitute at your Easter buffet.
Easter egg
If there’s one thing you definitely shouldn’t forget at Easter, it’s the Easter eggs. Swedish Easter eggs are less chocolatey than in other countries. The eggs themselves are not edible – they are made of cardboard with Easter-themed designs – and are filled with sweets.
These are easy to make vegetarian or vegan, just double-check that any sweets you include don’t contain animal-derived gelatin, and leave out the milk chocolate for any vegans.



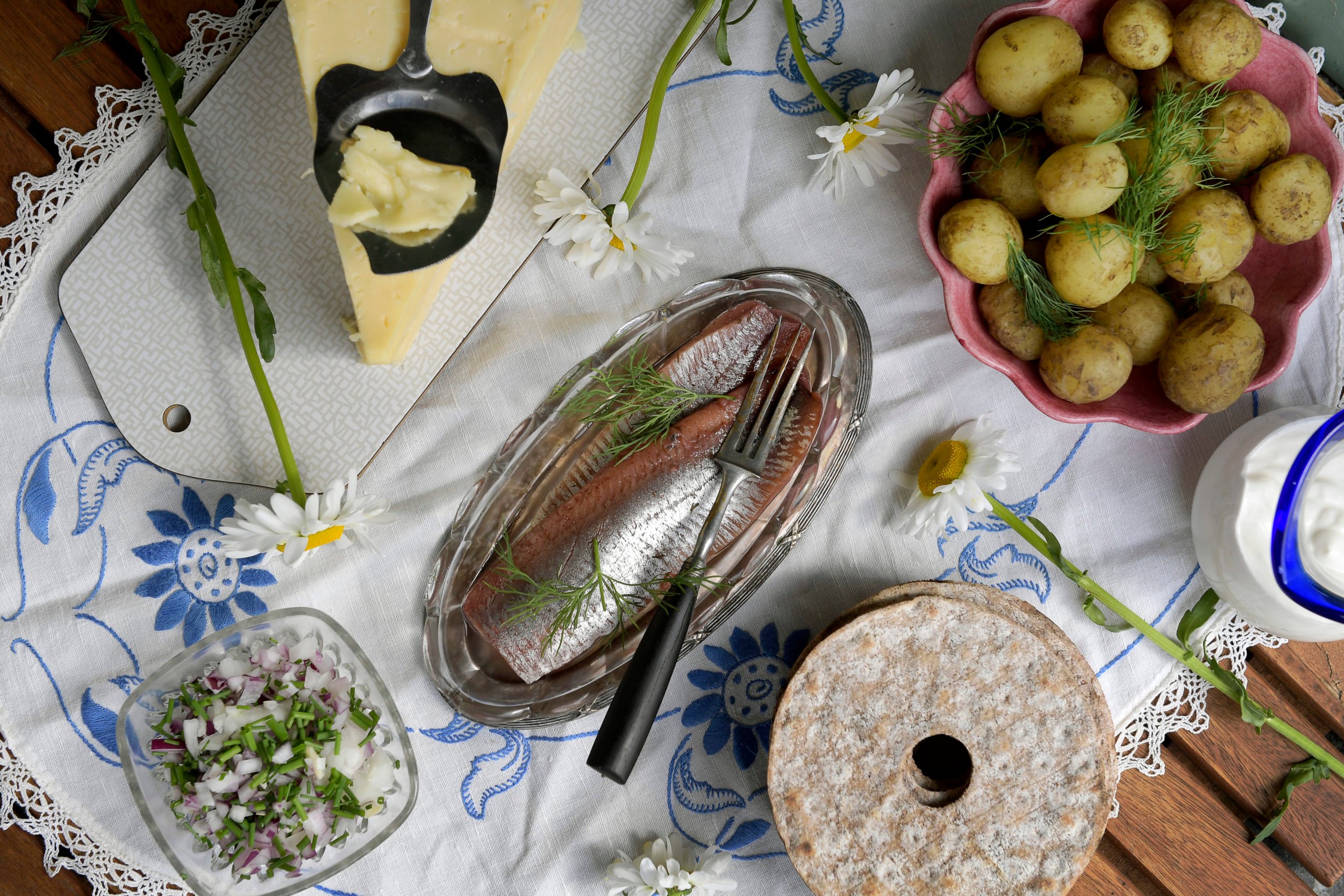



 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments