Demand for train travel has experienced a resurgence in recent years – a phenomenon that was accelerated by the pandemic.
As a result, overnight lines – long cut or stopped due to air travel – have become more popular, for business commuters and holiday makers alike.
EXPLAINED: How to find cheap train tickets in Switzerland
Standard trips have also bounced back in popularity.
The following tool, developed by German computer programmer Julius Tens, shows you how far you can get from each Swiss city.
Travel: What compensation you are entitled to if your train is cancelled in Switzerland?
There are of course more direct connections from larger cities, but the map does illustrate how well connected Switzerland actually is.
Simply enter the main train station of the city in which you live and you will be presented with a map of your options.
Unfortunately, anyone wanting to emulate the orient express and head all the way to Istanbul will be unable to do so direct from Switzerland (other than expensive private options).
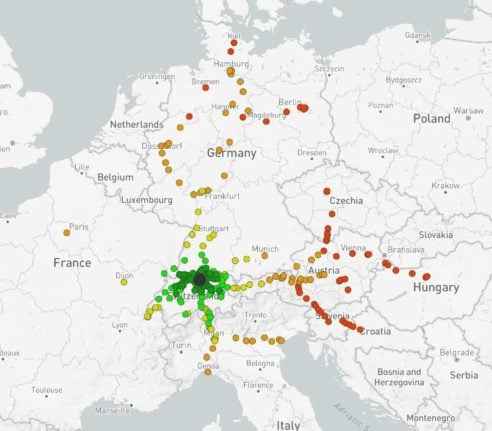
Zurich
Zurich offers by far the most destinations of any Swiss city, which makes sense when you consider its size and its location.
Connections to the east are particularly prevalent in Zurich, with direct trains to Prague, Budapest, as well as several cities in Austria, Croatia and Slovenia.
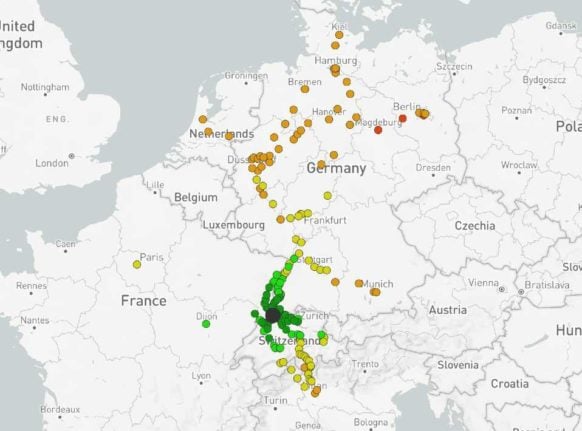
Basel
Basel might not be Switzerland’s largest city, but its central location means there are plenty of far away destinations on offer.
RANKED: Where are Switzerland’s best and worst train stations?
You can travel as far as Amsterdam, while Paris, Berlin and Kiel are also available via a direct trip. In fact, it appears that there are more direct trains to German cities from Basel than from Zurich.
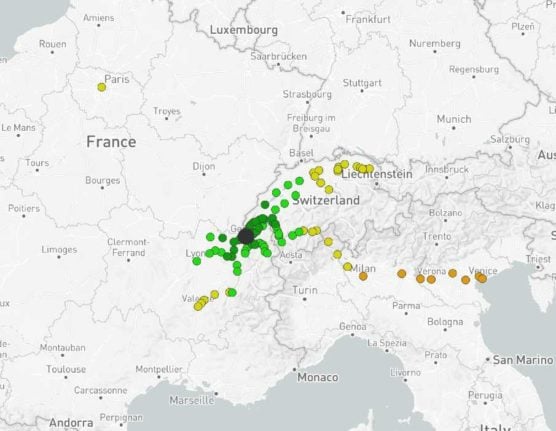
Geneva
Geneva, with its western location, doesn’t offer as many trips north or east as Basel and Zurich.
While you can get direct to Paris and Lyon, even getting to Germany direct is impossible from Geneva.
MAP: Return of night trains across Europe comes a step closer
There are however a number of Italian destinations you can get to from Geneva (but strangely not Italian-speaking Switzerland – for that you’ll have to change).
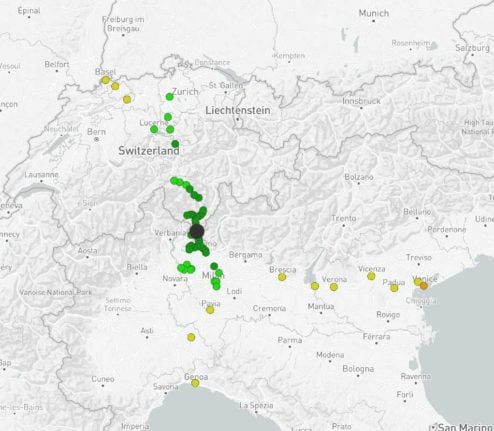
Lugano
Lugano doesn’t offer as many direct trains as the other Swiss cities. In fact, other than Switzerland, the only other places you can travel to direct area in Italy.
Venice, Milan, Genoa and Verona are some of your options in Italy, while you can also travel to Zurich, Basel and a handful of other Swiss cities.
To get to Geneva however, you’ll need to change trains.



 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments