
BORDER
Norway opens up to Swedish tourists… so long as they’re from Gotland
Norway will allow travel to and from all regions of Finland, Sweden and Iceland that have an 'acceptable' infection level – a criterion that rules out every region in Sweden apart from the island of Gotland.
Published: 12 June 2020 15:21 CEST
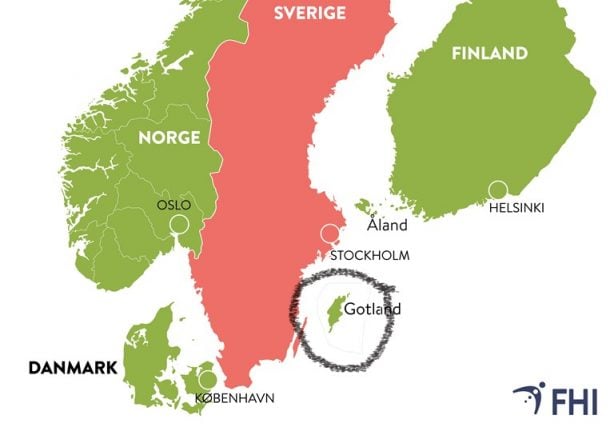
Just one small island region of Sweden meets the criteria. Photo: FHI/The Local
At a press conference on Friday afternoon, Bjørn Guldvog, the head of Norway's directorate of health, said that the guidelines drawn up meant that the whole of mainland Sweden would remain off limits until infection rates declined.
“In Sweden, the epidemic situation is unfortunately such that we can only now open up for leisure travel to and from Gotland,” he said, according to a report by state broadcaster NRK.
All regions of Denmark, Iceland, and Finland currently meet the criteria.
Prime Minister Erna Solberg conceded that the results of the new assessments would be unwelcome to those wishing to travel to and from Sweden.
“I realise this is a big disappointment for some people. But the restrictions are based on objective criteria that are the same for everyone,” she said at the press conference.
READ ALSO:
Solberg said the new guidelines would allow Norway to now open up for leisure travel to and from every country in the Nordic region, including Finland, Sweden and Iceland. It opened up to Danish citizens at the end of last month.
“But this only applies to regions with an acceptable reproduction number,” she added.
The Norwegian Institute of Public Health has assessed each region in the Nordics on the basis of their incidence rate over the past 14 days, and based on the percentage of positive samples over the past 14 days.
But it has also applied 'qualitative criteria', judging regions on the extent to which those with even mild symptoms are tested, on how good their contract tracing system is, and on the quality of information given out to travellers.
It has produced a new set of advice for international travel and a map, showing which regions in the Nordic countries meet the criteria and which do not.

Solberg said that the criteria will allow Norway in future to open up for and shut down to different regions as the level of infection in them fluctuates, with the NIPH publishing new regional assessments every fortnight.
“Let me emphasise – this is not just about where to spend the holidays this summer. We must plan for travel restrictions to last over time,” she said.
In a small ray of good news for those wishing to travel to and from Sweden, Bent Høie, Norway's health minister, said that several regions bordering Norway were currently close to meeting the criteria, meaning that they could see controls lifted when the situation is reevaluated in two weeks' time.
Solberg warned that the new system could mean a region of another Nordic country is ruled off limits at short notice, forcing Norwegians to cancel planned trips or to unexpectedly have to spend ten days in quarantine on their return.
“If you are planning a holiday outside Norway, you must also be aware that quarantine can be reintroduced at short notice if the infection situation changes while abroad,” she said.
The announcement came a day after Finland opened its borders to all of the Baltic and Nordic states except Sweden.
Url copied to clipboard!


 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments