In hopes of getting more people to cycle, the ‘Mai à vélo’ will offer thousands of cycling events and ‘challenges’ across France from May 1st to 31st.
The scheme began in 2020 and has been supported by the French ministries of environment and sports, with the goal of encouraging carbon-free forms of transportation.
In 2023, there were over 4,000 Mai à vélo events, with over 100,000 people participating in the activity challenges.
What types of events will there be?
From workshops to learn how to repair your own bicycle to group rides and bicycle exchanges, there will be plenty of different types of events across the country.
They can be hosted by schools, businesses, local authorities, associations and even just groups of friends.
If you are interested in hosting your own event, you will first need to make an account and register your plans.
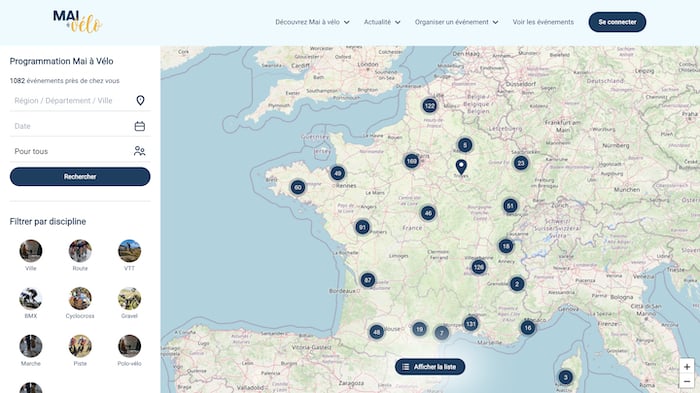
To find events near you, check out the interactive ‘Mai à vélo’ map.
Cycling on the rise
France, and particularly the city of Paris, have invested more into bike lanes over the last few years.
The study by the Institut Paris Region, an urban planning agency, found that more Parisians were opting for bicycles (accounting for 11.2 percent of trips) than cars (4.3 percent of trips).
READ MORE: How France will splash another €250 million on national ‘bike plan’
Walking was still the most common option (53.5 percent), followed by public transport at 30 percent.
Nevertheless – Paris launched its first ‘plan vélo’ in 2015 and its second phase started in 2021, with a budget of €180 million and the goal of making France’s capital ‘100 percent bicycle-friendly by 2026’.
On top of that, during the 2024 Olympic Games, the city will offer over 415 kilometres of bicycle lanes, plus thousands of new parking stations across the city and nearby Games venues. You can download the map of bicycle lanes on the Anticiper les jeux website.
Grants for purchasing a bicycle in France
The French government opted to extend their bonus vélo grant to 2027, in an effort to encourage non-polluting transport options.
Previously, the aid was only available to those buying new bikes, but in 2024 authorities opened it up to second-hand bicycles under certain conditions.
While it is means-tested, the financial aid is open to non-French nationals (though you must be resident in France and have a tax number in order to access the grants).
Depending on your financial situation and the bicycle you want to purchase, you may be eligible for assistance varying between €150 and €2,000.
If eligible, you can use it for plenty of different types of bicycles – from standard and electric bikes to cargo bikes, plus those adapted for people with disabilities.
READ MORE: Explained: The financial aid to buy a bike in France
Where should I cycle in France?
If affordable bicycles and fun events are not enough to entice you, perhaps you will be convinced by the dozens of beautiful bicycle routes criss-crossing the country and the warm, spring weather.
For example – you might consider the ‘Voie des Vignes’ cycle path which goes from Beaune to Santenay to Nolay.
The 22km Voie des Vignes (Way of the Vines) meanders its gentle way along vineyard paths, crossing the Unesco World Heritage-listed Climats of Burgundy.
There is also the Vallée du Loir cycle path, which is a 330 km track (the V47) that starts at the source of the river between Beauce and Perche and ends of the banks of Loire at Angers, passing by a fair share of castles.



 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments