Under one of the most liberal drug laws in Europe, adults in Germany are now allowed to carry up to 25 grams of dried cannabis on them and cultivate up to three marijuana plants at home.
“From our point of view, the law as it is written is a disaster,” Katja Seidel, a therapist at a drug addiction centre in Berlin, told AFP.
“Access to the product will be easier, its image will change and become more normalised, especially among young people,” Seidel said, adding that she expects to see an increase in cannabis use “at least initially”.
The government says decriminalising weed will hit the black market and reduce the spread of contaminated cannabis.
Health Minister Karl Lauterbach, a physician himself, acknowledges cannabis can be “dangerous” especially for people under the age of 25 whose brains are still developing.

READ ALSO: KEY POINTS: What to know about Germany’s partial legalisation of cannabis
Medical experts say cannabis use among young people can affect the development of the central nervous system, leading to an increased risk of developing psychosis and schizophrenia.
Lauterbach has promised a major campaign to educate youngsters about the health risks and boost prevention programmes, but it remains unclear how much money the government plans to spend and how effective it will be.
The new legislation has some safeguards to protect young people, including a ban on smoking cannabis within 100 metres (328 feet) of a school, kindergarten, playground or sports centre.
Reaching young people
Seidel, who works at the Tannenhof Berlin-Brandenburg drug rehabilitation organisation, is one of just two staff members who visits schools in the capital and surrounding areas to talk to young people about drug addiction and prevention.
To reach all pupils in the region, “at least 10 employees” would be needed, she told AFP.
The Addiction Prevention Centre in Berlin, run by the local authorities, also wants more resources poured into raising awareness.
It shouldn’t be the case that students learn about the dangers of cannabis consumption “just by chance”, said Janis Schneider, who works for the centre.
Health Minister Lauterbach has promised that the government’s campaign will explain, for example, “that children and young people who start smoking weed are much less likely to graduate from high school”.
The federal centre for health education, linked to the health ministry, told AFP it will “assume its responsibility by expanding its prevention offers”.
The planned media campaign however hasn’t convinced critics. “It doesn’t resonate with them, it will never work,” said Boris Knoblich, a spokesman for the Tannenhof Berlin-Brandenburg organisation.

“What works is someone who goes in, talks to them over a coffee, without a teacher there,” he said.
The southern state of Bavaria meanwhile is testing an online training course for teachers on how to approach the topic in the classroom.
READ ALSO: Why is Germany’s cannabis draft law so controversial?
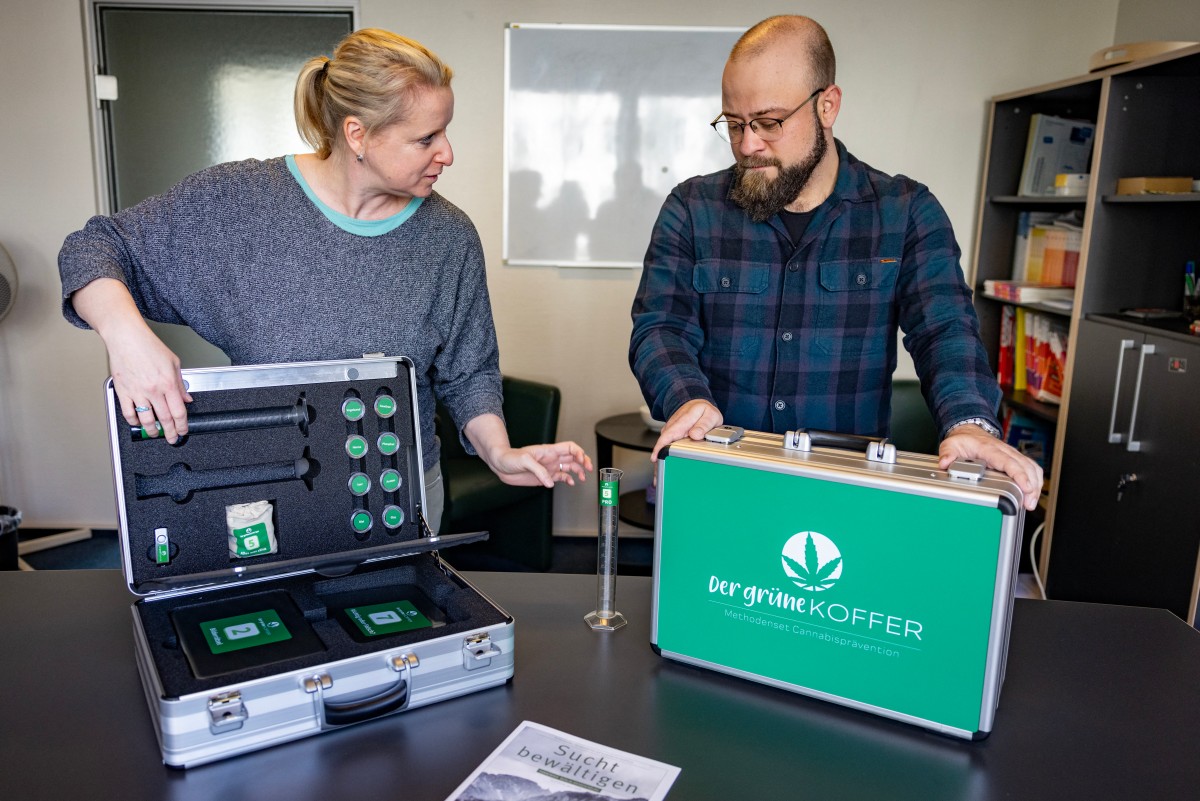
Prevention kits
In Berlin, staff from the Tannenhof organisation bring a prevention “kit” with them on their school visits: a green suitcase emblazoned with a cannabis leaf. It contains information sheets, games and material for activities.
Students are asked to insert coloured balls into two tubes that represent arguments for and against cannabis use, resulting in a visual representation of the cons outweighing the pros in the long term.
“We spend at least three hours with them in a relaxed atmosphere. This allows students not to self-censor,” said Pascal Noack from Tannenhof Berlin-Brandenburg.
According to official statistics from 2021, 8.8 percent of adults in Germany aged 18-64 admitted to consuming cannabis at least once in the preceding 12 months.. Among people aged 12-17, that number rose to nearly 10 percent.



 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments