If you’re travelling by rail
Sweden usually schedules railway maintenance work for national holidays, as fewer people are travelling to work, and Easter – with the arrival of warmer temperatures – tends to be the start of the rail works season in the southern half of the country.
The Swedish Transport Administration provides a detailed breakdown of Easter work planned. We’ve summarised the main points below.
Stockholm
The Citybanan commuter rail system in Stockholm will be closed between Stockholm City and Odenplan between March 29th at 10pm and April 1st at 5pm, with Stockholm’s regional travel company SL promising replacement traffic.
All rail traffic between Jakobsberg in northwest Stockholm and Stockholm City will also be cancelled throughout March 29th and April 2nd.
Gothenburg
Maintenance work on the tracks between Partille and Alingsås and bridge repairs between Töreboda and Gårdsjö will see regional trains between Gothenburg and Alingsås and Gothenburg and Gårsjö cancelled between March 28th and April 1st. Replacement buses will be provided.
Buses will also replace trains between both Varberg and Halmstad and Kungsbacka and Gothenburg from 2pm on March 28th to 2pm on April 1st, as tracks and switches are connected as part of the Varberg tunnel project.
The Västtågen commuter train will still operate between Gothenburg and Kungsbacka, with the Öresundståg trains taking that route.
Work on the new Västlänken will also mean all trains between Gothenburg’s Central Station and the Gamlestaden station in the north of the city will be cancelled all day on March 29th and on April 1st until 2pm.
West coast
As well as the cancellations of trains between Halmstad and Kungsbacka (see above), trains will also be cancelled between Borås and Varberg between March 28th at 2pm and April 1st at 2pm, due to roadwork around Sundholmen. Replacement buses will be provided.
Work will continue on the tracks between Uddevalla and Stenungsund, while the most southerly part of the same track, between Ytterby and Gothenburg, will also be closed between Good Friday and April 1st at 2pm.
Central Sweden
Work at Karlstad’s main station could see trains cancelled between March 28th at 10pm and April 2nd at 5.20am.
East coast
The Stångådalsbanan railway between Linköping and Kalmar could see trains cancelled between March 30th at 2pm and March 31st at 3pm.
Here is a map of the planned work:
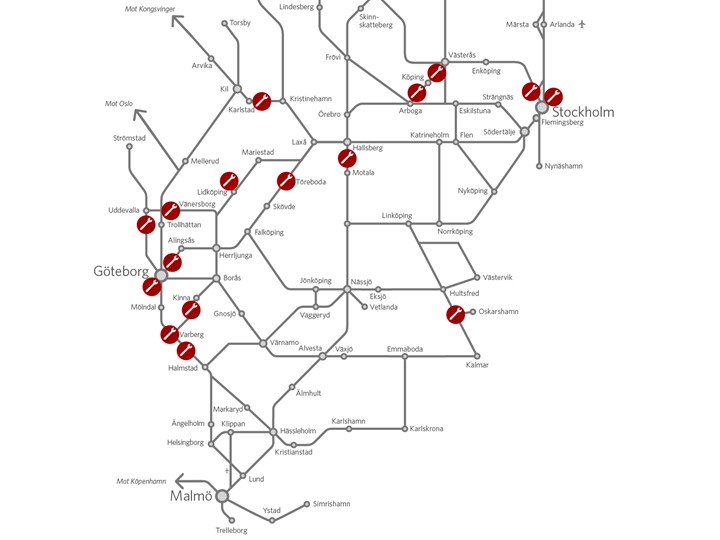
If you’re travelling by car
Easter is one of Sweden’s busiest travel holidays, and traffic tends to be concentrated to a few days, rather than spread out as at Christmas and Midsummer.
That means queues should be expected. It’s good to plan your journey in advance, allow extra time and make stops to rest.
The E4 road between Gävle and Tönnebro tends to be particularly busy as travellers head to and from the mountains for their Easter ski trip.
The good news for those travelling by car is that this year, no major roadworks are planned over Easter — mainly because the holiday falls so early this year that temperatures are still too close to freezing across much of the country, making it difficult to lay down new tarmac.
If you’re travelling by air
This year, there are no strikes directly affecting airports or airlines in Sweden, but industrial action in Spain and the UK might affect Easter travel if you are venturing abroad.
Workers at airports in Valencia and Madrid, two of Spain’s busiest, have announced that they will strike over the Easter period. At Madrid-Barajas airport, the UGT union has called a strike by employees of the Platform Management Service (SDP) for Wednesday 27th and Friday 29th March between 7am-12pm.
At Valencia airport, flights could be affected between Thursday March 28th and Monday April 1st, between 11am-13am, when workers will walk out and protest outside the Terminal 1 building in Manises.
The Lufthansa airline struck a deal with ground staff on Wednesday, March 27th, averting the risk of strikes over the Easter holidays, which might have affected flights to and from Germany from Norway.
Finally, border force workers at the UK’s Heathrow Airport voted on March 22nd to strike over the Easter holidays, although walkouts will not happen until after April 8th, you won’t be affected if you are only travelling over Easter, but might be if you stay another week.



 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments