Births in Europe have reached their lowest point since the 1960s in 2022, as only 3.88 million babies were born compared to more double some sixty years ago, according to the EU statistical office Eurostat.
In the period 1961–2022, all countries (EU member states as well as EFTA countries Switzerland, Norway, Iceland and Liechtenstein) saw steady declining birth rates.
The highest level recorded was 6.8 million in 1964. By 2002, births had declined to 4.36 million, followed by a modest increase to 4.68 million in 2008, and a general downward trend after that year (except for 2021, during the pandemic).
Highest birth rates in France
On average, the total birth rate, the average number of children born per the lifetime of each woman, was 1.46 live births in 2022.
Among the European countries covered (see image below), France had the highest, at 1.79, even though the national statistics bureau reported in January that births in France fell in 2023 to their lowest annual number since World War II, with an average birth rate of 1.68 children for each woman.
Romania (1.71) and Bulgaria (1.65) followed. The lowest fertility rates in 2022 were recorded in Malta (1.08), Spain (1.16) and Italy (1.24).
Other countries were somewhat in between, with Sweden reporting a fertility rate of 1.53, Austria 1.55, Germany 1.46, Switzerland 1.39. In comparison, Italy’s fertility rate in 1960 was 2.4, Denmark’s 2.57, and Austria’s 2.69 (this value is not available for all countries).
The UK’s birth rate decreased to 1.49 children per woman in 2022 down from 1.55 in 2021.
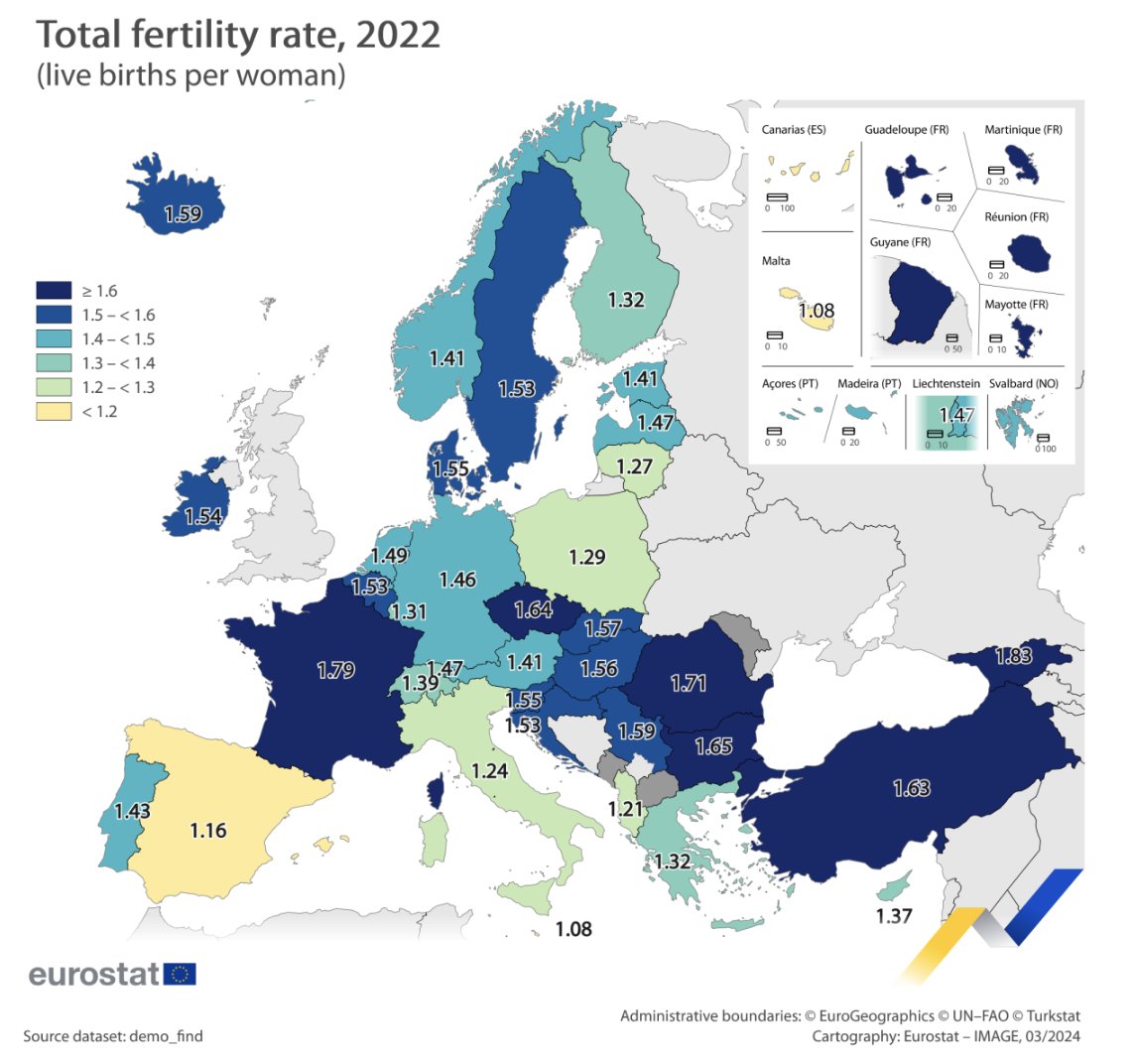
A fertility rate of around 2.1 live births per woman is considered to keep the population size constant in developed countries without migration.
In recent years, the EU population has decreased after decades of growth, mostly due to the hundreds of thousands of deaths caused by the Covid-19 pandemic. The current European Commission launched in 2021 a debate on Europe’s ageing society, suggesting steps for higher labour market participation, including more equality between women and men and longer working lives.
In countries such as Italy, there have been calls to increase financial support for those with young children, or measures addressing chronic problems which discourage or prevent Italians from starting a family at all.
But in France, President Emmanuel Macron’s plan to revive sluggish birth rate sparked an outcry, with feminists and left-wing politicians accusing him of seeking to control women’s bodies.
Having children later in life
Across Europe, it appears that many women are opting to have their first child at a later age than in the past, meaning that the possibility of other children is reduced.
The average age of women having their first child was in the EU in 2022 was 29.7 years (compared to 28.8 in 2013), ranging from 26.6 in Bulgaria and 27 in Romania, to 31.7 in Italy and 31.6 in Spain.
Eurostat notes that while the fertility rates for women below 30 years have declined since 2001, those for women aged 30 and above have risen. In 2001, the fertility rate for women aged 25-29 years was the highest among all age groups. In 2022, it was for 30–34-year-olds. The fertility rate for women aged 35 years and over is also increasing.
Foreign-born mothers
Eurostat also records that some 22 per cent of children in 2022 were born from foreign-born mothers, with most EU countries becoming increasingly diverse compared to 2013.
The highest proportion was 66 per cent in Luxembourg followed by 41 per cent in Cyprus. In Austria, Belgium and Malta, around one-third of children were born to foreign-born mothers. On the other hand, The lowest proportion was 2 per cent in Slovakia and Bulgaria.
This article was published in cooperation with Europe Street News.



 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
No statistics as usual for UK. Some former Yugoslav countries also have no statistics. Cannot be just an EU survey as Turkey is included.