Expecting a baby can be an anxiety-inducing experience, no doubt. Fortunately, Italy is rightfully famous for its healthcare system, which produces some of the world’s best maternal health outcomes.
Part of the secret to that success is a robust schedule of testing that residents can access for free as part of their pregnancy.
In fact, the amount of testing offered during pregnancy in Italy can be surprising to those who aren’t familiar with the Italian health service.
Here’s what to expect:
Getting started: the first appointment (6-11 weeks)
Before you can get any testing done, you will need to arrange for a first appointment with an obstetrician via a local hospital, private clinic, or family counselling center.
In the early stages, your pregnancy will be dated to the first day of your last menstruation, so be prepared to provide that date a lot. It will be included on all your paperwork as you go from provider to provider.
READ ALSO: Pregnancy in Italy: What are the options for public or private healthcare?
Your first appointment should generally be scheduled after the sixth week of pregnancy, so that the fetus is clearly visible on an ultrasound, and ideally before 11 weeks. Because there are sometimes delays in securing appointments, it makes sense to plan ahead as much as possible.
At this first appointment, you’ll get a general orientation to the process laid out below and be scheduled for future check-ups. You’ll get a basic physical and they’ll take a full medical history.
Then, you’ll be scheduled for your first battery of tests to establish a baseline of health and confirm your pregnancy.
On the first visit, or shortly thereafter, you’ll receive the following tests free of charge:
- A first ultrasound to confirm your pregnancy and determine the age of the fetus;
- A Pap (smear) test, if one has not been performed in the last three years;
- A series of blood tests to check for blood type, blood sugar, red cell antibodies (the Coombs test), rubella, toxoplasmosis, syphilis and HIV; and
- A urine test.
If you’re deemed at risk for Hepatitis C, chlamydia or gonorrhea, you may also receive tests for these as well.
The Bi-Test (11-14 weeks)
Starting at 11 weeks, you’ll be eligible for the so-called Bi-Test or Combined Test, which screens for common genetic and developmental disorders.
Until 2017, this test was only free for women over 35, but it’s since been made a standard part of pregnancy health screening in Italy.
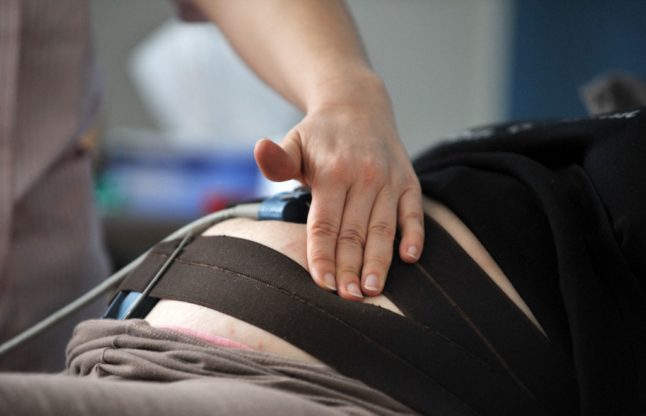
The non-invasive test involves an additional blood sample and ultrasound between 11 and 14 weeks that checks for abnormalities in the fluid beneath the fetus’ neck.
Because the test is only about 92 percent accurate, if it detects any issues, your physician will refer you for follow-up testing — either non-invasive DNA testing, which is more accurate, or an invasive amniocentesis procedure, which samples a small amount of cells from your amniotic fluid and provides a definitive positive or negative result.
READ ALSO: 15 practical tips for pregnancy in Italy
If you miss the window for the bi-test, there’s an optional non-invasive blood test known as the tri-test, available from the third trimester, that can screen for the same issues. It also tests for neural tube defects, another common disorder.
These tests are optional but are covered by the national health service. In practice though, whether you can access this test for free depends on whether there is a trained, public technician in your area.
In some regions, only the invasive tests can be performed in the public system.
Regular checkups
After these initial tests, you’ll be scheduled for regular checkups every month to 40 days. At these checkups, you’ll receive a basic physical and blood pressure check and your doctor may listen for the fetus’ heartbeat.
You’ll also be regularly tested for toxoplasmosis, rubella, and your blood glucose levels, so be prepared to roll up your sleeves a lot.

Sometime between 24 and 28 weeks, you’ll receive another urine test, and at 28 weeks, you’ll be scheduled for another round of the Coombs test, which checks for red cell antibodies.
All of these tests are simply part of ensuring your health and that of the baby is ideal as you head into the later stages of pregnancy.
Depending on your hospital or physician, you may also receive additional ultrasounds during this period. Most Italian women report receiving an average of 4 to 5 ultrasounds over the course of the pregnancy, despite only two being required by law.
Second ultrasound (19-21 weeks)
At minimum, your second ultrasound should occur between 19 and 21 weeks, and this is the big one — your fetus should be looking like a baby and you are likely to be able to determine the sex.
If you don’t want to know the sex of the baby, you should speak to your gynecologist in advance. They can withhold the information, or even provide it in a sealed envelope to a trusted friend if you are planning on organizing a reveal.
Third trimester: Tests, tests, and more tests
By the 28th week, you may be recommended for a follow-up ultrasound if your doctor has any concerns about the baby’s development.
You’ll also receive another blood test, including a Coombs test, and will be scheduled for tests for toxoplasmosis, Hepatitis B, HIV, syphilis, and vaginal streptococcus, to occur sometime between 33 and 38 weeks.
Lastly, you’ll also be required to do another urine sample between 33 and 38 weeks, to ensure you won’t have a urinary tract infection at the time of delivery.
More tests?
The above is just a baseline — your doctor may order additional tests if they are concerned about any aspect of you or your baby’s health.
If anything goes wrong with your pregnancy, you may be referred to specialist care. This should all be free of charge, so long as they are requested by a physician in the public system. (If you opt for private care, you may be required to pay fees for these same services.)
After delivery
The Italian national health service also covers postpartum care, including psychiatric screening and postpartum counselling. If you are experiencing signs of postpartum depression, it’s worth talking to your doctor about referrals to this care.
The cost of birthing and parenting courses are also covered by the government, so ask your physician about what is available in your area.
READ ALSO: Who can register for national healthcare in Italy?
All these tests are available free of charge to EU citizens regardless of whether or not they have an Italian health card (tessera sanitaria). Any non-EU citizens with a long-stay visa (permesso di soggiorno) may access them also with referral from a physician.
If you do not have a visa or are undocumented, you can access many of these services via a local family counselling center (consultorio familiare), which are obligated by law to provide care to all women irrespective of immigration status.
Keep in mind that if you opt for a private gynecologist or pregnancy clinic, you may have to pay extra for tests available for free from public hospitals. Price lists are rarely posted online, so do your research before choosing a provider.
For more information about healthcare during pregnancy in Italy, see the health ministry’s official website here.


 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments