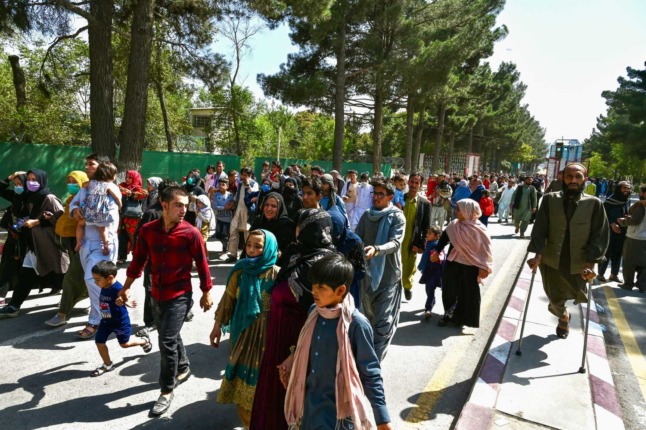
Austria’s interior minister said Wednesday he would lobby the EU to help set up “deportation centres” in countries neighbouring Afghanistan to take in Afghans deported from Europe.
Austria has insisted it wants to continue to deport Afghans whose asylum claims have been rejected or who have been found guilty of crimes and to discourage refugees fleeing the Taliban’s takeover of Afghanistan to come to Europe.
“It is important… that it continues to be possible to deport violent asylum seekers or refugees, so we need these deportation centres,” Interior Minister Karl Nehammer told reporters before meeting his EU counterparts.
Austria under conservative Sebastian Kurz has a hardline stance on migration, at odds with the chancellor’s current coalition partner, the Greens.
The Taliban seized Kabul on Sunday, taking power again in Afghanistan after two decades of war and sparking huge concerns globally about their brutal human rights record.
READ MORE: Will Austria accept more Afghani asylum seekers due to Taliban crisis?
Deportations paused temporarily
Vice Chancellor Werner Kogler on Monday evening said deportations to Afghanistan would no longer take place in line with the European Convention of Human Rights and asylum applications would continue to be accepted.
The Convention prohibits people from being deported back to a country where there is a risk of torture or a danger to life and limb.
However, when Kogler was asked directly if Afghan asylum seekers should be accepted in Austria, he said Austria should offer support, especially in protecting women. But he said he could not elaborate further, “because we do not rule alone”.
Interior Minister Karl Nehammer (ÖVP) has come under fire in recent days following comments that people would continue to be deported to Afghanistan as long as it was possible.


 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments