France recently introduced a new requirement for all property owners in France to fill in a property tax declaration.
This applies to anyone who owns property in France – whether it is their main residence or a second home – including those who live in another country.
You can find full details about the declaration and how to fill it in HERE.
But people who own their property through an SCI have run into problems with their declarations.
An SCI – société civile immobilière – is a non-trading real estate company made up of at least two people. Essentially, it allows people to own property such as a second home through shares of a company, rather than under their own name.
Most property owners have been told to fill out the declaration by simply going onto the website impots.gouv.fr, logging into their personal space and then clicking on Biens immobiliers (real estate) in the menu bar along the top of the website.
READ MORE: UPDATE: New French property tax declaration – your questions answered
The site should then list the property or properties in your name, and you can fill out the déclaration d’occupation for each, stating whether it is your main residence or a second home.
However, many SCI property owners have found themselves perplexed to not see their property show up after logging onto their personal space on the impots.gouv.fr website.
This is because, according to French tax authorities, owners of SCI properties should carry out the procedure on their “professional” space, rather than their personal space – since an SCI is technically a business that owns the property.
Anyone who runs a business in France will already have a ‘professional’ tax account, but SCI property owners will need to set one up in order to make the legally-required declaration.
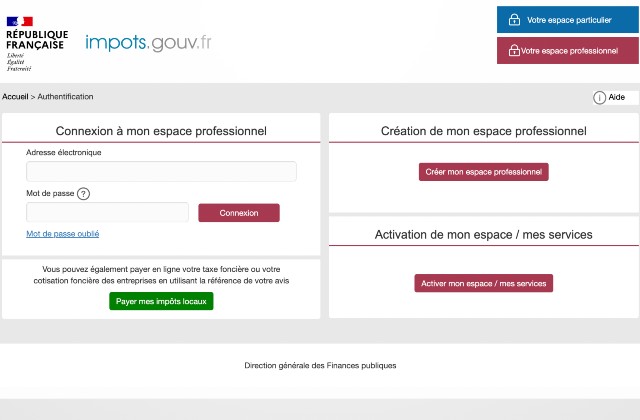
You can set one up by going to the website impots.gouv.fr and clicking “Votre espace professionel”.
Next, you will click “Créer mon espace professionel”. Fill out the required information, keep in mind you will need access to the SCI’s SIREN number and the company’s official email address.
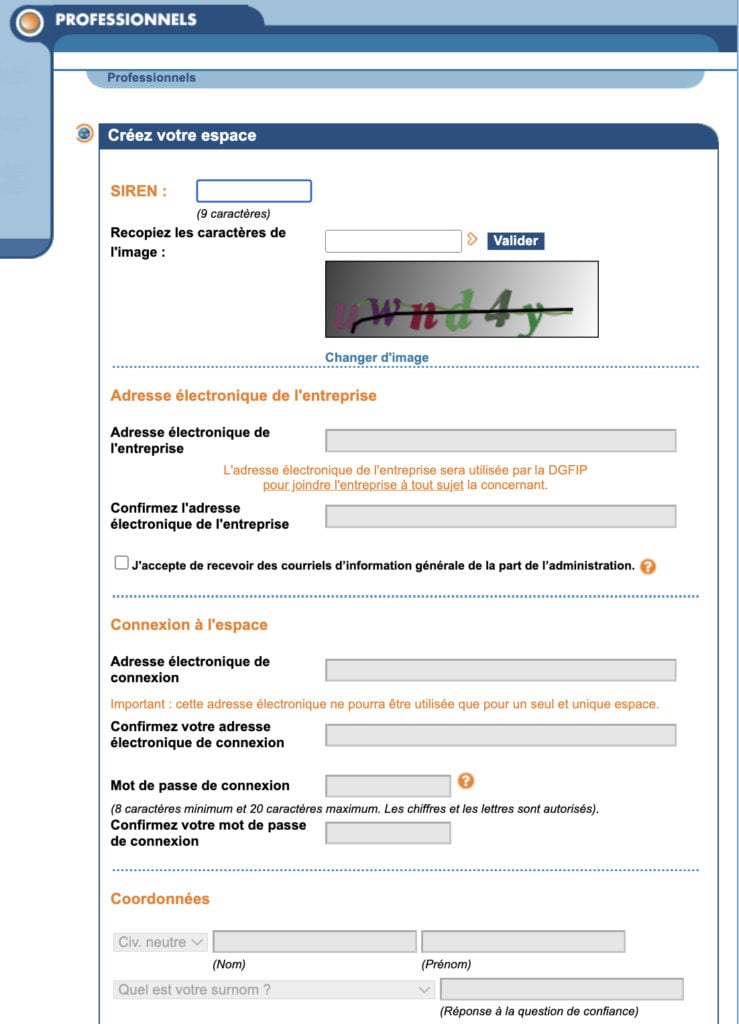
The tax office for your département will send you an activation code by post as soon as your space creation request has been validated. You will then have 30 days to activate your space and fill in your bank details. Once this is finished, you ought to be able to access the online service immediately.
READ MORE: EXPLAINED: The advantages and pitfalls of buying French property with an SCI
The deadline to have completed the declaration is June 30th, and people who have a property registered should receive notification from the tax office.
You will then receive your property tax bill in the autumn as usual.
This is a one-off declaration so you won’t have to do it every year – only when your situation changes, so for example if you sell the property, buy a new one or change from it being a second-home to your main residence.
READ MORE: What should I do if I want to dissolve my French property SCI?


 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Not trying to be a pain, but my Professional Space has been set up for my SCI owned apartment for three years already and there is still no link to do the tax declaration. Has anyone else had this problem?