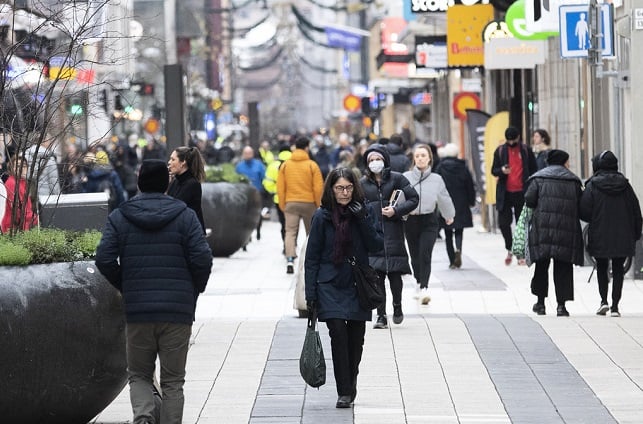
The capital Stockholm is once again at the epicentre of the epidemic and this week called on members of the public with medical training to help offset some of the burden on healthcare.
Lars Falk, a doctor at an intensive care unit at the Karolinska Hospital in Stockholm, told AFP the second wave had hit much harder than they expected.
“We got three different scenarios from the Public Health Agency this summer. We prepared for the worst, and it turned out twice as bad,” Falk told AFP.
While the Swedish capital is the worst-hit region in the country, many others are also seeing resources stretched thin. On Monday, the number of people receiving hospital care reached 2,406, near the peak of 2,412 on April 20th.
For now, the number of people in intensive care is still only at half the level seen in April, according to Sweden's National Board of Health and Welfare.
The total number of deaths associated with Covid-19 in the country of 10.3 million reached 7,802 on Wednesday, with more than 500 in the last week and over 1,800 since the beginning of November.
With very few coercive measures and no face mask rule, Sweden has stood apart by relying on citizens' “responsibility” and issuing only recommendations for individuals — with no sanctions if they are ignored.

A sign at a Malmö train station says: 'Thank you for avoiding journeys that are not completely essential. Save lives. Today too.” Photo: Johan Nilsson/TT
Authorities have tried to call for greater personal sacrifices as new cases have risen — notably urging people to limit social interactions to those in their household or a very small circle of friends.
However, some measures are binding, and on November 24th a ban on public gatherings of over eight people went into force, lowering the number from 50 as it had been throughout spring and summer.
“We become tougher, but I think we need to be even tougher than this,” intensive care doctor Falk said.
Contrary to media reports, the Scandinavian nation never targeted so-called herd immunity as part of its official strategy. But health officials did argue that the high level of spread in the spring should weaken any second wave.
“I think we will have a relatively low even spread during the autumn, with clusters in different places,” state epidemiologist Anders Tegnell told broadcaster TV4 in August.
That seemed to be borne out for a while, as the second wave hit later and deaths remained low in October. Tegnell stuck to his assessment that the country could do better than many others in Europe.
“With the expertise and tools we have in place in Sweden, there are good reasons to believe we can avoid that type of development,” Tegnell said at the end of the month.

Photo: Henrik Montgomery/TT
Despite criticism, Prime Minister Stefan Löfven has refused to call the strategy a failure, arguing it is too early to make a final assessment. But in an interview with daily Aftonbladet on Tuesday, Löfven also said he felt many experts had underestimated the second wave.
“I think most in the profession did not see such a wave incoming, there was instead talk of different clusters,” he said.
An independent commission appointed by the government did however conclude that the strategy failed in its effort to protect the elderly in care homes, a lapse already conceded by authorities. Over 90 percent of coronavirus deaths in Sweden have been among those aged 70 and up, and nearly half of all deaths have been in retirement homes.
In part the response has also been constrained by legislation, including a guarantee on freedom of movement enshrined in the constitution.
The government is preparing a temporary, one-year “pandemic law” it aims to have in place by March 2021, which will empower ministers to limit the number of people in public places and regulate businesses and services by restricting opening hours or even shutting them down.
Sweden, like the rest of the EU, also hopes to start vaccinations at the end of December.
With 600,000 people lined up as priority candidates for January, the government expects to be able to offer vaccination to the entire population around the middle of next year.
By Marc Preel
READ MORE:


 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Hasn’t it been obvious that the Swedish strategy DOES NOT WORK?? It did not work in the Spring, and it definitely is not working in this Autumn/Winter period. It’s a disaster.