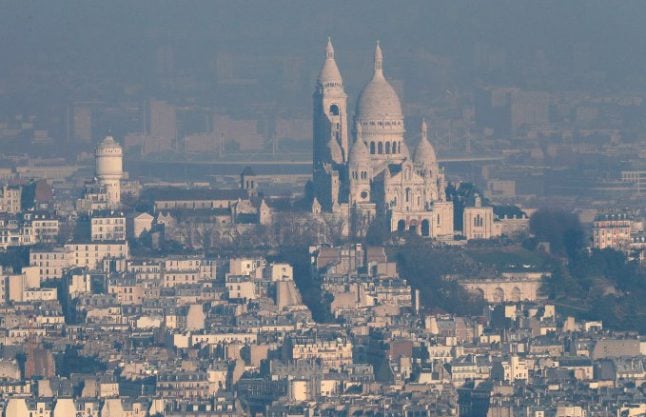
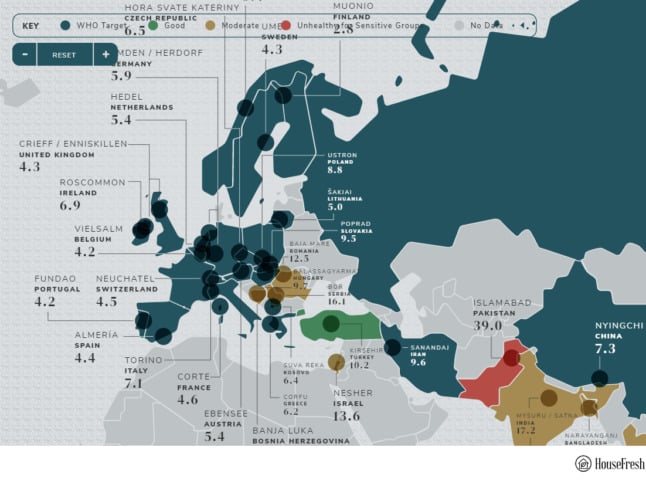
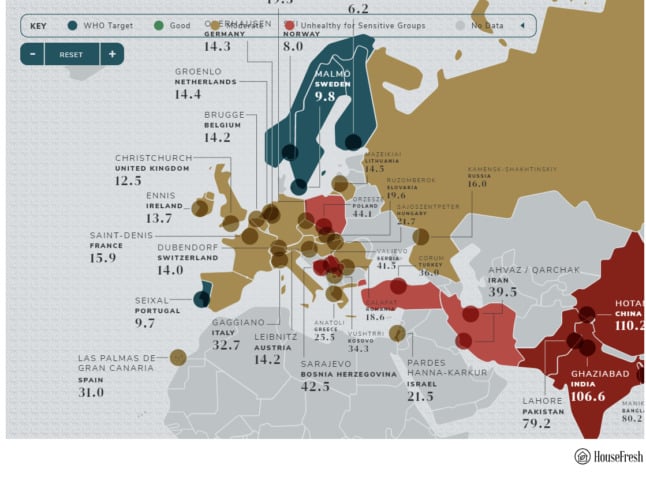
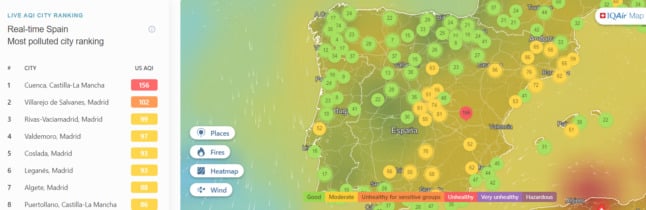
Paris and its surrounding towns are suffering their worst and most prolonged winter pollution for at least ten years, the Airparif agency which measures air quality said on Wednesday.
The peak is due to the combination of emissions from vehicles and from domestic wood-fires as well as near windless conditions which means pollutants have not been dispersed, the agency said.
Traffic restrictions have been imposed on the capital since Tuesday morning meaning around half of drivers have to leave their cars at home each day or face a fine.
On Tuesday it was only motorists with even-numbered registration plates who could drive in Paris and 22 of the surrounding communes, while on Wednesday it was those with odd-numbered plates.
Authorities have also taken the step of making all public transport in the region free, so commuters can travel on the RER trains, the Metro, buses and tramways without needing to buy a ticket.
Air pollution is Paris is not a new problem and has regularly raised its head over the years.
In March 2014 authorities were forced to introduce similar traffic restrictions and make public transport free due to a pollution spike that lasted several days.
At the time environmental groups in the French capital said “enough was enough” and lodged a legal complaint forcing judges to investigate the high levels of pollution.
The claimed the dirty air was “putting people's lives in danger”. A report at the time said the air in Paris was like a room with eight smokers in it.
READ ALSO: IN PICTURES: Paris cloaked in smog as air pollution rises

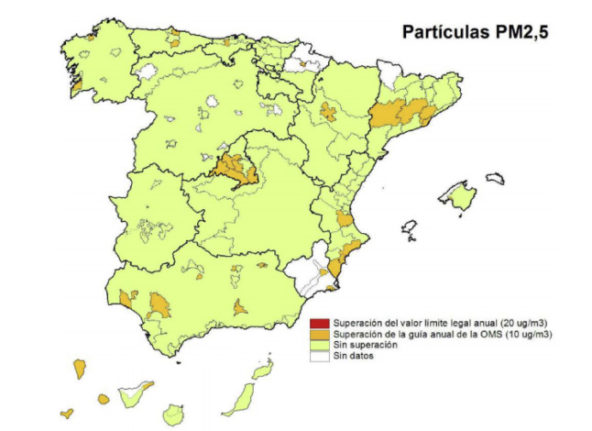
The pollution in and around Paris is generally caused by the particles known as PM 10 that are emitted by vehicles as well as by chimneys of houses and factories.
Such particles are too tiny to be filtered in the mouth and nostrils, and so embed themselves in the lungs more easily, and can have significant negative health effects.
According to the Airparif agency the three major sources of emissions in the greater Paris region for both air pollutants and greenhouse gas emissions are: “the residential and tertiary sector, due to the heating, transportation and industry.
“These three sectors represent nearly 95 percent of CO2 emissions,” says the agency.
“These pollutants have widely documented effects,” Airparif says on its website.
“On human health (long and/or short time effects. Mainly cardiorespiratory problems), on the global and local environment (river acidification and eutrophication in some European regions, ozone impact on crop yields, acid rains) and on buildings (blackening and encrustation).”
Airparif have issued advice for how to avoid being exposed to the potential impact of the air pollution including not doing too much strenuous exercise. CLICK HERE for more tips on how to avoid being exposed.
Paris has taken steps to ease pollution including introducing a obligatory new system of stickers to highlight the most polluting vehicles.
Drives of those vehicles will have to leave them at home during future pollution spikes or face financial penalties. The system will be brought in in January.
Paris mayor Anne Hidalgo has also moved to ban diesel vehicles and the most polluting trucks from the city.
And in a bid to push cars out of the city she has closed the right bank of the river to traffic, although opponents say it has just moved the traffic jams elsewhere.
In December 2014 Paris was meant to impose a ban on log fires at home, but it was ditched at the eleventh hour by Environment Minister Segolene Royal.
“They made us believe it was more polluting than diesel,” Royal said at the time.
“Consumer groups have approached me about this prohibition and I am not in favour of it,” she added.
“It seems excessive. I’m all for encouraging people to become aware of pollution but I don’t want it to be due to one decision, that I find a little absurd.”



 Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Please whitelist us to continue reading.
Member comments